Diaphragm Breathing: A Natural Approach to Anxiety


Intro
Diaphragm breathing, a technique often overlooked in the realm of anxiety management, presents an intriguing method for those seeking relief from chronic stress and anxiety. As anxiety becomes increasingly prevalent in today’s fast-paced society, understanding effective management strategies is vital. This article delves into the nuances of diaphragm breathing, enmeshing it within the broader framework of anxiety treatment options.
By addressing the physiological mechanisms at play, we reveal how diaphragm breathing can significantly influence the autonomic nervous system, thereby promoting a state of calm. Furthermore, the psychological benefits derived from regular practice cannot be understated. Those who practice this controlled breathing technique often report enhanced mental clarity and emotional stability.
Through this analysis, we aim to present a detailed exploration of diaphragm breathing, its scientific underpinnings, practical methodologies, and its promising role within therapeutic settings. Our focus extends to the integration of mindfulness, as well as actionable strategies for daily practice, all aimed at improving overall mental well-being.
Preamble to Diaphragm Breathing and Anxiety
The link between breathing and anxiety is often overlooked in modern discussions of mental health. This introduction sets the foundation for understanding how diaphragm breathing can be an effective tool in managing anxiety. Through careful breath control, individuals can bring physiological and psychological benefits to bear on the experience of anxiety.
Diaphragm breathing, also known as abdominal or belly breathing, uses the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs. This technique fosters deeper, fuller breaths that can help in reducing anxiety symptoms. Understanding this connection is essential. Anxiety can trigger shallow, rapid breathing patterns, which may exacerbate feelings of panic or distress. By learning to tap into diaphragm breathing, individuals can shift their breathing patterns, thereby influencing their emotional state.
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions that go beyond occasional worry. They are often characterized by persistent fear or apprehension that can interfere with everyday functioning. Common types include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Each type has unique symptoms and may require different management strategies.
"Anxiety disorders are the most commonly diagnosed mental health issues in the world, affecting millions of individuals each year."
Recognizing the physiological aspects of anxiety permits a more comprehensive approach to treatment. Symptoms can include increased heart rate, shortness of breath, and feelings of being overwhelmed. These facets illustrate the importance of developing breathing techniques that can mitigate these physiological responses.
Diaphragm Breathing: A Definition
Diaphragm breathing involves engaging the diaphragm for more efficient air intake. Unlike shallow chest breathing, this method promotes full oxygen exchange, which is beneficial for overall health. When one inhales deeply and slowly through the nose, the diaphragm moves downwards, allowing the lungs to expand completely.
Practicing diaphragm breathing can lead to various benefits, including:
- Reduction of stress hormones: By promoting relaxation, it can decrease levels of cortisol, a hormone linked to stress.
- Improved oxygen flow: Enhanced oxygen delivery helps boost overall energy levels and improve mental clarity.
- Calming effect: It engages the parasympathetic nervous system, which counters the fight-or-flight response often associated with anxiety.
The Physiology of Breathing
Understanding the physiology of breathing is vital. It connects the body's physical functions with mental health, especially regarding anxiety. Breathing is not merely a biological process. It also serves as a bridge between our mind and body. This section examines how diaphragm breathing influences emotional well-being by altering physiological functions.
Mechanism of Diaphragm Contraction
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lung. Its primary role is to facilitate breathing. When we inhale, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. This increase in chest cavity volume allows air to flow into the lungs. This contraction is vital for efficient oxygen exchange.
Key elements to note about diaphragm contraction include:
- Increased lung capacity: When the diaphragm contracts, it enables deeper breathing. Deep breaths improve oxygen intake.
- Stimulation of vagus nerve: The diaphragm contraction activates the vagus nerve. This process triggers a relaxation response within the body.
- Coordination with abdominal muscles: The diaphragm often works in conjunction with abdominal muscles. This coordination aids in better control of breath and stabilizes core pressure.
"Deep, controlled diaphragm breathing can transform the body's response to stress events."
Engaging the diaphragm leads to physiological changes that lower heart rate and improve overall calmness. Practicing diaphragm breathing regularly can enhance its benefits, making it easier to access during times of anxiety.
Role of the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) governs involuntary body functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It has two main parts: the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- Sympathetic system: Often referred to as the 'fight or flight' system. It becomes active during stress, leading to an increase in heart rate and breathing rate.
- Parasympathetic system: Known as the 'rest and digest' system. This system promotes relaxation and recovery.
Diaphragm breathing plays a crucial role in balancing these nervous system responses. By practicing this breathing technique, individuals can engage the parasympathetic system. This engagement helps in calming the body and reducing anxiety symptoms.
Benefits include:
- Lower stress hormones: Controlled breathing significantly reduces cortisol levels, which are often elevated during stress.
- Improved blood circulation: By enhancing diaphragm function, overall blood flow increases. This can positively influence mental state.
- Enhanced brain function: Deep breathing improves oxygen supply to the brain. This can facilitate clearer thinking and improved emotional regulation.
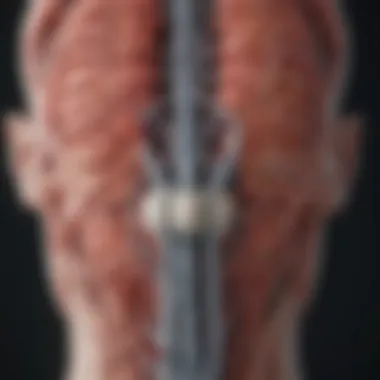
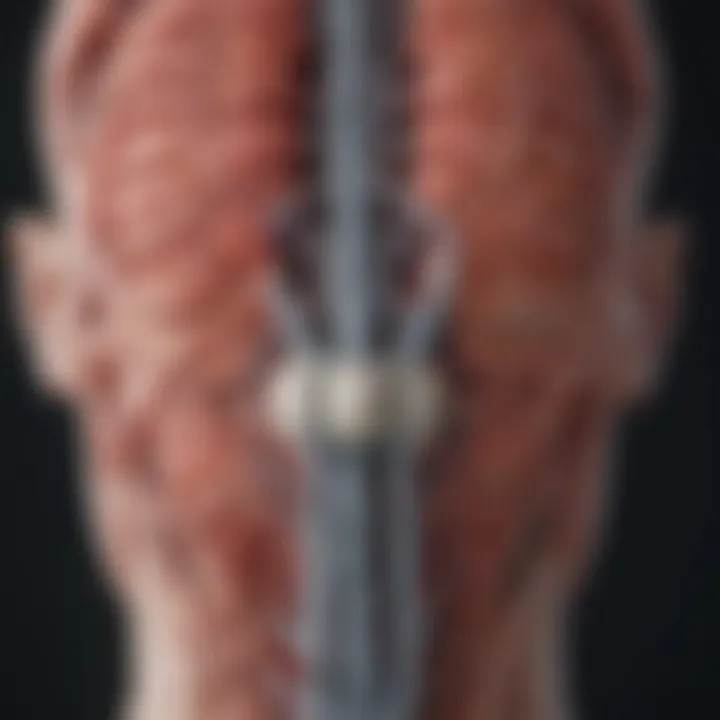
In summary, understanding diaphragm contraction and its role within the autonomic nervous system highlights the physiological impact of breathing on anxiety. By effectively managing our breath, we can alter our body's stress response. This understanding lays essential groundwork for implementing practical techniques for anxiety management.
Why Diaphragm Breathing Reduces Anxiety
Diaphragm breathing is a technique that can significantly impact anxiety management. Understanding its relevance is crucial for those who seek effective coping strategies. The benefits of this approach are multifaceted, extending beyond mere relaxation. It engages physiological mechanisms that facilitate emotional regulation and stress reduction.
Impact on Stress Response
The body's stress response is tightly linked to breathing patterns. During stressful situations, many people engage in rapid, shallow breathing. This can exacerbate anxiety. In contrast, diaphragm breathing encourages deep, deliberate breaths, activating the parasympathetic nervous system. This transition helps counteract the body’s stress response, leading to a calming effect.
By slowing the heart rate and lowering blood pressure, diaphragm breathing can effectively decrease the levels of the stress hormone cortisol. An individual practicing this technique may experience a marked reduction in anxiety symptoms.
"Breathing techniques like diaphragm breathing can create a noticeable shift in how we respond to stress, offering a simple yet powerful tool for anxiety management."
Enhancement of Mindfulness
Engaging in diaphragm breathing cultivates mindfulness. Mindfulness refers to the practice of maintaining a present-focused awareness. When one concentrates on the mechanics of breathing, it diverts attention from anxious thoughts.
Practicing this technique inevitably encourages a focus on the here and now. Such focus helps in recognizing and accepting feelings without judgment. This has been shown to improve emotional resilience.
Additionally, integrating diaphragm breathing in daily routines leads to increased self-awareness. This shift not only aids in managing anxiety but fosters a positive mental state.
In summary, diaphragm breathing plays a vital role in reducing anxiety by influencing both physiological and psychological domains.
Practical Techniques for Diaphragm Breathing
Understanding and utilizing diaphragm breathing techniques plays a critical role in managing anxiety. The significance of practical techniques cannot be overlooked, as they provide actionable steps that individuals can incorporate into their routines. By mastering these techniques, one can foster a sense of control over their breathing, which is essential for reducing anxiety symptoms. The following sections will detail basic steps for practice and methods for daily incorporation.
Basic Steps for Practice
To begin the practice of diaphragm breathing, it is essential to establish a comfortable environment. Choose a quiet space where distractions are minimized. Here are important steps to effectively practice diaphragm breathing:
- Find a Comfortable Position: Sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Ensure your back is straight and shoulders relaxed.
- Place Your Hands: Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. This will help you feel the movement of your diaphragm.
- Inhale Deeply: Breathe in slowly through your nose. Focus on expanding your abdomen while keeping your chest as still as possible. Count to four as you inhale.
- Hold Your Breath: Briefly hold your breath for a count of two. This can enhance focus and helps the body adjust to deeper breathing.
- Exhale Slowly: Breathe out slowly through your mouth or nose, allowing your abdomen to fall. Again, count to six during the exhalation.
- Repeat the Cycle: Continue this process for five to ten minutes, allowing your body to relax with each breath cycle.
As these steps become more familiar, practitioners can adjust the timing of inhalation and exhalation based on personal comfort levels.
Incorporating Diaphragm Breathing into Daily Life
Integrating diaphragm breathing into everyday routines can enhance mental health and well-being. Here are effective strategies to make diaphragm breathing a habitual practice:
- Morning Routine: Start your day with a few minutes of diaphragm breathing. This sets a calm tone for the day.
- Before Stressful Situations: Use this technique before meetings or presentations to reduce anxiety. Engaging in focused breathing for a few minutes can stabilize feelings of nervousness.
- During Breaks: Take short breaks throughout the day to practice. This can be particularly beneficial at work or during studies, as it can reset your mental state.
- Before Sleep: Engage in a session of deep breathing before bedtime to facilitate a more restful sleep. The calming effect helps signal to the body that it is time to unwind.
- Mindfulness Practices: Combine diaphragm breathing with meditation or yoga. This enhances mindfulness and allows for greater emotional balance over time.
"Consistent practice integrates the power of breath into daily life, creating a foundation for emotional resilience."
In summary, practical techniques for diaphragm breathing not only provide a toolkit for anxiety management but also help establish healthy coping mechanisms. This can lead to improved emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Research Evidence Supporting Diaphragm Breathing
The significance of research evidence supporting diaphragm breathing lies in its ability to substantiate the claims surrounding its efficacy in anxiety management. Understanding the scientific foundations can foster a greater acceptance of these techniques in clinical and everyday settings. This section will examine specific clinical studies and overarching meta-analyses that illuminate the mechanisms and benefits derived from diaphragm breathing practices.
Clinical Studies and Findings
Clinical studies focusing on diaphragm breathing often indicate notable decreases in anxiety symptoms among participants who incorporate this technique into their routine. One specific study published in the journal The Journal of Clinical Psychology highlighted that patients engaging in diaphragm breathing reported a marked reduction in panic attacks compared to those who did not practice this method. Researchers attributed these improvements to enhancements in both parasympathetic activation and hormonal regulations.
In another study, participants with generalized anxiety disorder practiced controlled breathing exercises, which included diaphragm breathing over eight weeks. The outcome demonstrated a significant reduction in the severity of anxiety and related symptoms. Moreover, these individuals exhibited improvements in their overall quality of life.
These findings suggest that diaphragm breathing does not merely act as a sporadic tool but can be integrated as a holistic approach to managing anxiety disorders.
Meta-Analyses on Breathing Techniques and Anxiety


Meta-analyses offer a broader perspective by evaluating multiple studies collectively, thereby providing more robust conclusions. One notable meta-analysis published in Psychological Bulletin reviewed various breathing techniques, focusing on their effects on anxiety. This comprehensive study found that diaphragm breathing, when compared to other methods, yielded the most consistent and positive results for anxiety reduction. The analysis indicated that participants engaged in diaphragm breathing experienced greater emotional stability and lower anxiety levels consistently.
Additionally, the synthesis of data from multiple clinical trials demonstrated that combining diaphragm breathing with mindfulness processes further enhanced its effectiveness. Individuals practicing both techniques showed improvements not only in anxiety management but also in areas such as concentration and emotional regulation.
This convergence in research supports the idea that diaphragm breathing is a viable therapeutic option for those dealing with anxiety and suggests promising avenues for integrating these practices into existing therapeutic frameworks.
"Scientific evidence reinforces the value of diaphragm breathing as an effective strategy for anxiety reduction. It further calls for deeper integration of such methodologies in mental health treatment protocols."
Diaphragm Breathing in Therapeutic Settings
Diaphragm breathing holds considerable significance within therapeutic contexts. Its integration into various treatment modalities provides a multifaceted approach to anxiety management. This technique acts as a bridge connecting physiological regulation and psychological relief. Due to its emphasis on controlled breathing, it offers a clearer path toward emotional stability and stress reduction. The following sections will delve deeper into how diaphragm breathing is woven into psychological treatments and its vital role in stress management programs.
Integration into Psychological Treatments
Incorporating diaphragm breathing into psychological treatments is a practice rooted in the principles of somatic therapy. This approach recognizes the mind-body connection. By targeting physiological responses, therapists can help clients gain self-regulation skills that are essential for managing anxiety.
- Therapeutic Practices: Many practitioners include diaphragm breathing in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) sessions. This helps clients develop awareness of their breath patterns, often linked to anxiety episodes. Improving breathing technique can enhance emotional resilience, providing clients with tools to cope during moments of distress.
- Skill Development: Clients can learn and practice diaphragm breathing alongside other therapeutic skills. This can amplify the effectiveness of established techniques like mindfulness and exposure therapy. With enhanced respiratory control, clients may find an increased sense of empowerment over their anxiety symptoms.
- Evidence-Based Support: Research supports the use of breathing techniques as adjuncts to psychotherapy. Clinical trials have demonstrated that individuals who practice diaphragm breathing report lower anxiety levels and improved outcomes in overall mental health.
Breathing techniques, such as diaphragm breathing, are increasingly recognized for their effectiveness in psychological settings, adding depth to traditional therapies.
Role in Stress Management Programs
The role of diaphragm breathing in stress management programs cannot be understated. Stress often triggers the fight or flight response, leading to shallow, rapid breaths. By emphasizing diaphragm breathing, these programs aim to reset the body’s stress response.
- Physical Benefits: Engaging in diaphragm breathing promotes relaxation. The technique stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, which dampens stress responses and lowers heart rate. This physical calm can reduce the cognitive load associated with anxiety.
- Daily Practice: Stress management programs routinely incorporate practices that encourage integrating diaphragm breathing into the daily routine. When individuals practice regularly, they can develop a more stable baseline for emotional regulation. This means they are better prepared to tackle stress when it arises.
- Workshops and Group Sessions: Many stress management programs now include workshops or group sessions centered on breathing exercises. Participants can share experiences and techniques, fostering a supportive environment. This communal aspect can enhance motivation and adherence to the practice.
Contrasting Other Breathing Techniques
When discussing the impact of breathing techniques on anxiety, it is essential to look at various methods available. Understanding how diaphragm breathing contrasts with other techniques can enhance a person’s approach to managing anxiety. Different breathing methods yield distinct physiological and psychological effects. Knowing these differences allows individuals to choose the most effective strategy for their condition.
Diaphragm Breathing vs. Chest Breathing
Diaphragm breathing involves using the diaphragm muscle, which is located beneath the lungs. This technique allows for deeper inhalation and encourages full oxygen exchange. On the other hand, chest breathing relies on the contraction of muscles in the chest area. It tends to be shallow and rapid, which may not facilitate adequate oxygen distribution throughout the body.
Some key differences include:
- Depth of Breathing: Diaphragm breathing provides deeper breaths. Chest breathing often leads to more shallow inhalations.
- Physiological Impact: Diaphragm breathing promotes relaxation and decreases stress levels. Chest breathing might increase anxiety due to its association with rapid, superficial breathing.
- Oxygen Efficiency: Using the diaphragm improves oxygenation in the body. Chest breathing often results in less effective oxygen uptake.
In essence, choosing diaphragm breathing over chest breathing can significantly influence one’s anxiety levels and overall physiological response. It is crucial to prioritize methods that favor the body’s natural systems, reducing stress instead of exacerbating it.
Comparing Techniques: Efficacy and Usage
Different breathing techniques have their own merits, often tailored to individual needs. While diaphragm breathing stands out for its advantages in anxiety management, other methods also exist.
- Abdominal Breathing: Focuses on the expansion of the abdomen while inhaling. It is quite similar to diaphragm breathing but may not always emphasize diaphragm usage.
- 4-7-8 Technique: Involves inhaling for four seconds, holding for seven seconds, and exhaling for eight seconds. This structured approach can benefit individuals seeking quick relaxation, though it may not promote the same depth of breath as diaphragm breathing.
- Box Breathing: This method combines inhalation, retention, exhalation, and pause, each lasting for the same duration—often four seconds. It is a useful way to manage acute anxiety but may not allow for the same diaphragm engagement.
"The choice of breathing technique should align with personal comfort, anxiety levels, and specific therapeutic goals."
The Psychological Effects of Controlled Breathing
Controlled breathing, particularly diaphragm breathing, holds significant importance in managing anxiety. This practice connects both physiological and psychological processes, revealing a pathway to alleviate symptoms associated with anxiety disorders. The effects of breathing techniques extend beyond physical relaxation; they can fundamentally shift mental states by fostering a sense of calm and aiding in emotional balance.
Reduction in Anxiety Symptoms
Diaphragm breathing has been shown to help reduce anxiety symptoms effectively. When individuals engage in this type of controlled breathing, they instruct their body to activate the parasympathetic nervous system. This system is known for promoting a state of relaxation, which counters the often heightened stress responses characterized by anxiety.
Research indicates that individuals who practice diaphragm breathing report lower levels of anxiety. Studies suggest that, during episodes of heightened anxiety, the body becomes tense, and breathing can become shallow. By consciously deepening and slowing the breath, the body can signal a reduction in fight-or-flight responses, leading to a calmer mental state.
In practical terms, when someone takes deep breaths, it helps to lower heart rates and decrease cortisol levels, a hormone related to stress. As a result, the overall feelings of anxiety diminish. In a controlled environment, such as therapy or mindfulness sessions, the benefits become even more pronounced, allowing individuals to focus and utilize breathing as a tool against anxiety symptoms.

Improvement in Emotional Regulation
Another notable effect of diaphragm breathing is its influence on emotional regulation. Emotional regulation refers to the ability to monitor, evaluate, and modify emotional reactions. Controlled breathing practices assist individuals in gaining better awareness of their emotional states. This awareness leads to improved management of intense feelings such as fear, anger, or sadness.
When one engages in diaphragm breathing, the act itself serves as an anchor during emotional turmoil. It encourages mindfulness, allowing individuals to observe their emotions without becoming overwhelmed. Instead of reacting impulsively, they learn to pause, breathe, and respond thoughtfully to situations.
Various studies highlight the link between regulated breathing and emotional stability. Consistent practice of diaphragm breathing can help individuals build resilience to stressors, enabling them to maintain composure in challenging situations. This skill is particularly valuable for those managing anxiety, as it fosters a sense of control over one's emotional landscape.
"Effective breathing techniques can empower not just the mind, but also the entire emotional framework of a person."
Challenges in Practicing Diaphragm Breathing
Practicing diaphragm breathing can offer significant benefits for managing anxiety. However, several challenges may hinder individuals from effectively implementing this technique. Understanding these challenges is crucial for practitioners, therapists, and individuals seeking relief from anxiety. It highlights the need for tailored strategies to address barriers and misconceptions surrounding diaphragm breathing. Thus, recognizing these challenges can lead to more effective practices and better mental health outcomes.
Common Obstacles and Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about diaphragm breathing that may prevent individuals from trying this technique. Some think it is just another trend in wellness, dismissing its clinical backing. Others believe that they cannot learn proper diaphragm breathing techniques due to previous failures with other methods.
- Lack of Awareness: Many individuals are simply unaware of diaphragm breathing and its benefits. This ignorance limits their willingness to explore the technique.
- Misunderstanding the Process: There is confusion around what constitutes proper diaphragm breathing. Some may inadvertently practice shallow chest breathing, leading to frustration.
- Physical Limitations: For certain individuals, physical limitations can create barriers to effective diaphragm breathing. Conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can make proper breathing challenging.
- Time and Consistency: Integrating any new practice into daily life requires time and dedication. Many may not prioritize this, viewing it as an additional task rather than a necessity.
"Breathing is the bridge between the body and mind—overcoming obstacles in breathing can enhance mental clarity and decrease anxiety."
Overcoming Barriers to Practice
Recognizing and addressing these obstacles is essential for successful adaptation of diaphragm breathing. Here are some strategies that can aid individuals in overcoming barriers:
- Education and Awareness: Providing clear, informative resources about diaphragm breathing helps demystify the technique. Understanding how it impacts anxiety can motivate individuals to give it a try.
- Guidance from Experts: Working with therapists or practitioners who specialize in breathing techniques can provide personalized feedback. This guidance ensures proper technique and builds confidence.
- Gradual Integration: Start with short sessions of diaphragm breathing, gradually increasing duration as comfort grows. This helps to build consistency without overwhelming the practitioner.
- Support and Community: Connecting with support groups or online communities can provide encouragement. Sharing experiences and challenges can foster a sense of belonging and motivate individuals to continue practicing.
In summary, while there are genuine challenges in practicing diaphragm breathing, acknowledging these obstacles allows individuals to develop tailored strategies. This will ultimately lead to a sustainable practice that can enhance mental well-being and regulate anxiety.
Future Directions in Research and Practice
The need for continued exploration into diaphragm breathing and its effects on anxiety is significant. As mental health issues become more prevalent, understanding effective intervention methods is crucial. Recent findings suggest that diaphragm breathing could enhance emotional regulation and reduce anxiety symptoms. However, gaps still exist in the literature regarding optimal practices and long-term efficacy.
Expanding Understanding of Breathing Techniques
A deeper understanding of breathing techniques is essential for maximizing their therapeutic potential. Research should focus on various methodologies related to diaphragm breathing. This might include exploring the following aspects:
- Variations in Practice: Different cultural and historical practices of diaphragm breathing need to be assessed. This includes examining Tibetan chanting or yoga techniques that utilize breath control. Comparing these with modern clinical implementations may reveal unique benefits.
- Physiological Responses: There is growing interest in quantifying physiological responses to diaphragm breathing. Mechanisms behind heart rate variability and changes in emotional states while practicing controlled breath need clarification.
- Longitudinal Studies: Healthcare professionals need more data from long-term studies that follow individuals practicing diaphragm breathing. This research could provide insights concerning sustained mental health benefits over time.
Interdisciplinary Approaches to Anxiety Management
The integration of diaphragm breathing into broader therapeutic frameworks may yield significant benefits. Better collaboration between psychology, physiology, and alternative medicine can enhance our knowledge of how controlled breathing influences anxiety management. Possible directions include:
- Combining Techniques: Studies should explore combining diaphragm breathing with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices. Understanding how these integrations impact overall anxiety reduction could create more robust treatment protocols.
- Training for Professionals: Educating mental health practitioners on the mechanics and benefits of diaphragm breathing is crucial. Proper training can ensure that professionals incorporate this technique into their treatment plans effectively.
- Patient Awareness Programs: Encouraging patients to understand the role of breath in managing anxiety can promote self-efficacy. Copies of findings from recent studies, available through platforms like Britannica, should be shared to encourage interest.
"The intersection of disciplines can lead us to discover complementary approaches in managing anxiety. By bridging the gaps, we can provide individuals with more comprehensive strategies that fit their needs."
In summary, focused efforts in research and practice can enhance our understanding of diaphragm breathing and its application. Expanding the knowledge base in this area is crucial to improving anxiety management strategies.
Closure
The conclusion plays a vital role in summarizing the entire discussion on diaphragm breathing and its significance in anxiety management. It serves to reaffirm the importance of controlled breathing techniques, particularly diaphragm breathing, highlighting how it can provide a sense of calm and improve emotional regulation.
One of the key elements discussed throughout the article is the physiological and psychological impact of diaphragm breathing. By emphasizing the connection between controlled breathing and the autonomic nervous system, readers can understand how this technique activates the parasympathetic system, promoting relaxation. The benefits of incorporating this practice into daily life are profound, as it not only helps reduce anxiety symptoms but can also enhance overall mental well-being.
Recap of Key Points
- Diaphragm Breathing Defined: A technique that involves deep breaths using the diaphragm, enhancing oxygen flow and promoting relaxation.
- Physiological Mechanism: Engaging the diaphragm can influence the autonomic nervous system, reducing the stress response.
- Psychological Benefits: Enhanced mindfulness and improved emotional regulation lead to significant reductions in anxiety levels.
- Practical Techniques: Simple steps can be integrated into daily routines to help manage anxiety.
- Research Evidence: Various studies and meta-analyses support the efficacy of diaphragm breathing in therapeutic settings.
Final Thoughts on Diaphragm Breathing
In concluding this exploration, it becomes clear that diaphragm breathing is not just a simple breathing exercise but a profound tool in anxiety management. As we navigate an increasingly stressful environment, incorporating this technique can provide a much-needed respite. It is worth noting that while diaphragm breathing is beneficial, it should complement other therapeutic approaches for holistic anxiety management. By cultivating awareness of one's breath, individuals can reclaim a sense of control over their anxiety and enhance their mental health.
Emphasizing the scientific evidence supporting this practice may encourage wider acceptance and application among those struggling with anxiety. As research in this field expands, future explorations may provide deeper insights into integrating diaphragm breathing into various therapeutic practices.















