Understanding Ulcer Psoriasis: In-Depth Insights

Intro
Ulcer psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease that affects a considerable number of individuals worldwide. It is a specific subset of psoriasis characterized by ulceration and a distinct clinical presentation. Understanding ulcer psoriasis requires exploring various aspects including its pathophysiology, symptoms, and treatment options. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide for students, researchers, educators, and professionals engaged in understanding this complex condition.
The prevalence of ulcer psoriasis highlights the need for more effective management strategies and innovative treatment options. Recent research in this area brings forth exciting discoveries related to its underlying mechanisms. These developments promise to enhance our understanding of ulcer psoriasis and offer hope for improved interventions.
Recent Advances
Latest Discoveries
The landscape of ulcer psoriasis has seen significant changes in recent years. Researchers are actively uncovering how genetic and environmental factors interact to trigger the disease. For example, specific mutations in genes related to immune response have been identified as potential contributors to the severity of ulcer psoriasis.
Current studies focus on inflammatory pathways that play a role in the disease's progression. For instance, overactivity of the NF-kB proteins and interleukins significantly influences the formation of ulcerative lesions. Understanding these molecular targets opens new avenues for targeted therapies and personalized medicine.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements have revolutionized how ulcer psoriasis is diagnosed and managed. Non-invasive imaging techniques are now being used to assess skin structure and function more precisely. For example, optical coherence tomography is helping dermatologists visualize the extent of skin involvement and monitor treatment responses.
Digital health solutions, such as telemedicine applications, are also gaining popularity. They enable patients to access specialists without visiting in person, benefiting those with mobility issues or other barriers to care.
Methodology
Research Design
This article employs a systematic review methodology, compiling findings from various studies on ulcer psoriasis. It draws data from peer-reviewed journals, clinical trials, and meta-analyses to present an overview of the current understanding of the disease.
The research design also considers both qualitative and quantitative studies to provide a balanced view of clinical experiences alongside statistical observations.
Data Collection Techniques
Data for this review was gathered from various sources. Key techniques included:
- Reviewing clinical trial outcomes,
- Analyzing patient-reported experiences from healthcare platforms,
- Utilizing meta-analysis strategies to evaluate overall trends in therapy efficacy.
This multi-faceted approach ensures a thorough examination of ulcer psoriasis and its management, allows for informed conclusions, and supports future research directions.
Ulcer psoriasis presents unique challenges for patients, often impacting their quality of life. Understanding its complexities and recent advancements is crucial for effective management.
Prelims to Ulcer Psoriasis
Ulcer psoriasis is a complex and multifaceted skin disorder. Understanding this condition goes beyond mere acknowledgment of its symptoms or treatments. This article aims to elucidate the intricacies of ulcer psoriasis, thereby illuminating its significance in dermatological research and patient care.
Definition and Overview
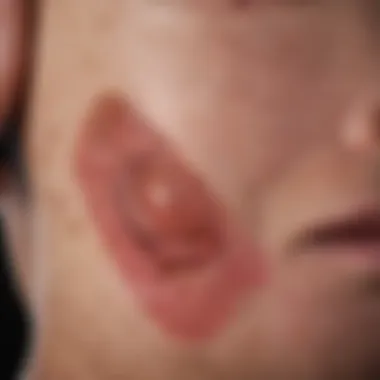
Ulcer psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis characterized by the formation of ulcers, particularly in areas where skin experiences friction or pressure. These ulcers often lead to discomfort and can severely impact one's daily activities. The pathology of ulcer psoriasis is rooted in an overactive immune response, leading to rapid skin cell proliferation and inflammation. This results in the formation of plaques that can eventually become ulcerated.
The condition is not just a skin issue; it is a chronic inflammatory disease with systemic implications. Recent studies suggest that patients with ulcer psoriasis are at a higher risk for comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome. As such, understanding ulcer psoriasis is crucial for developing more effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Historical Context
The understanding of psoriasis has evolved significantly over centuries. In ancient times, it was often misclassified or attributed to various factors without a solid scientific basis. The term "psoriasis" was first coined in the 18th century, derived from the Greek word "psora," meaning itch. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that the autoimmune nature of the disease began to be recognized.
With advancements in medical research, our comprehension of ulcer psoriasis has expanded. The introduction of biologic therapies in the late 20th century marked a turning point. These treatments specifically target underlying mechanisms of disease, offering new hope to patients who previously had limited options.
Understanding the historical context enriches the conversation surrounding ulcer psoriasis today, providing insights into the progress made and the pivotal challenges that remain. By comprehending where we started, we can appreciate the journey towards effective management of this chronic condition.
Pathophysiology of Ulcer Psoriasis
The pathophysiology of ulcer psoriasis is critical for understanding how this complex condition manifests and progresses. It involves multiple biological processes that affect the skin and immune system. Insight into these mechanisms helps in devising effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. Understanding this topic also fosters better patient education about their condition, allowing individuals affected by ulcer psoriasis to make informed decisions regarding their treatment.
Immune System Involvement
Ulcer psoriasis is primarily an immune-mediated disorder. The immune system plays a central role in its pathogenesis. In healthy skin, there is a balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals. In ulcer psoriasis, this balance is disrupted. Immune cells, such as T-cells, become activated and release pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines include tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-17 (IL-17), which contribute to inflammation and skin cell proliferation.

Consequently, affected patients experience increased blood flow and infiltration of immune cells into the skin. This reaction leads to the formation of psoriatic plaques and ulcerative lesions. The immune response in ulcer psoriasis is non-specific, meaning any trigger can exacerbate the condition. Understanding immune system involvement is essential for developing targeted therapies that can modulate this response, offering patients much-needed relief.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction
Another significant aspect of ulcer psoriasis is skin barrier dysfunction. The skin serves as a physical barrier protecting against environmental insults and pathogens. In this condition, the barrier's integrity is compromised. Factors contributing to barrier dysfunction include excessive skin cell turnover and an impaired lipid composition within the stratum corneum.
When the skin barrier is weakened, it loses its ability to retain moisture, leading to dryness and increased permeability. As a result, irritants and allergens can penetrate more easily, causing further inflammation. This cycle perpetuates the condition, making it difficult for those affected to manage symptoms. Addressing skin barrier dysfunction is crucial in treatment plans, as restoring its integrity can significantly affect symptom severity and overall health.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors also play a vital role in the development of ulcer psoriasis. Research indicates that certain genes may predispose individuals to this condition. Twin studies reveal a higher concordance rate for ulcer psoriasis among identical twins than fraternal twins, highlighting a genetic component. Specific gene variants, especially those related to immune function and skin barrier, have been associated with heightened susceptibility.
Understanding these genetic underpinnings allows researchers to identify potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches. Furthermore, genetic research could pave the way for groundbreaking therapies that target the root causes of ulcer psoriasis rather than merely managing symptoms. This insight emphasizes the importance of genetics in the comprehensive understanding of ulcer psoriasis and its future management.
Clinical Manifestations
In the context of ulcer psoriasis, clinical manifestations represent a focal point for understanding how the disease affects individuals on a day-to-day basis. This section is vital as it outlines how the condition presents itself, enabling better diagnosis and treatment pathways. Recognizing these manifestations can help patients and healthcare providers identifiy the harbingers of the disease, facilitating timely medical intervention. Furthermore, awareness of clinical signs and symptoms can significantly improve patient education and management strategies.
Symptoms and Signs
Ulcer psoriasis comes with a set of distinctive symptoms, which can vary in presentation from person to person. The most common presentations include:
- Red patches of skin: These may appear on various body areas, including elbows, knees, and the scalp.
- Ulcerative lesions: These are critical to identify as they indicate active disease and can be quite painful.
- Itching or burning sensations: Many sufferers experience severe discomfort that can worsen as the lesions spread.
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails: Nail abnormalities often accompany the skin manifestations.
These symptoms may not only inflict physical pain but also take a toll on the mental well-being of the patient. Social stigma or discomfort may arise from the visible signs of the condition, leading to emotional distress.
Types of Ulcerative Lesions
The ulcerative lesions specific to ulcer psoriasis can be categorized into a few types, each with its own characteristics:
- Localized ulcers: These lesions are limited in area and typically found on the skin's surface.
- Generalized plaques: Larger areas may be affected, leading to extensive ulceration.
- Pustular lesions: In some cases, these can develop, filled with pus and often causing further inflammation.
Each type of lesion can impact the treatment approach and overall management of ulcer psoriasis. Healthcare providers must differentiate between these forms to tailor appropriate therapies.
Associated Conditions
Ulcer psoriasis does not exist in vacuums; it often correlates with other health conditions, which can complicate both diagnosis and management. Common associated conditions include:
- Psoriatic arthritis: Joint inflammation that can arise alongside the skin symptoms, often causing mobility issues.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Increased risk is associated with chronic inflammation linked to psoriasis.
- Metabolic syndrome: Factors like obesity and diabetes often coexist with ulcer psoriasis, increasing overall health risks.
Recognizing these associated conditions is critical for comprehensive care. Healthcare professionals must adopt a holistic approach, considering all aspects of a patient's health while treating ulcer psoriasis.
Understanding the clinical manifestations of ulcer psoriasis ensures that effective treatment strategies can be employed, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Diagnosis of Ulcer Psoriasis
A correct diagnosis is essential for managing ulcer psoriasis effectively. The complexity of this condition often requires a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. Timely and accurate diagnosis can lead to better treatment outcomes. Moreover, understanding the underlying mechanisms helps in tailoring individual management plans. A misdiagnosis can result in inappropriate treatment and a worsening of symptoms, highlighting the significance of precise diagnostic measures.
Clinical Assessment Techniques
Clinical assessment techniques for ulcer psoriasis involve a combination of visual inspection and patient history. Medical practitioners usually start with a physical examination, looking at the skin condition to identify key characteristics typical of ulcer psoriasis. These may include erythema, scaling, and ulcerative lesions.
Patients are asked about the duration of symptoms, previous treatments, and family history of psoriasis or similar conditions. This information helps the physician form a comprehensive overview. Sometimes, tools like the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) are used to quantify the severity of the disease.
Healthcare professionals must also consider other factors, such as individual comorbidities. Psychological aspects, including the patient’s emotional state and any associated stress, play a role in the assessment. These assessments aid in determining the current impact of the disease on the individual’s life.
Histopathological Evaluation
Histopathological evaluation involves analyzing skin biopsies under a microscope. This step can confirm the diagnosis of ulcer psoriasis by revealing characteristic histological features. Typical findings include hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and inflammatory cell infiltrates.
During this evaluation, dermatopathologists closely examine the skin sample. They look for acanthosis or thickening of the epidermis and examine the extent of inflammation present in the dermis. A clear diagnosis can prevent overlap with conditions that present similar symptoms, such as contact dermatitis or fungal infections. This precision in histopathology is vital in managing treatment options effectively.
Differential Diagnosis


Differential diagnosis is crucial in ensuring that ulcer psoriasis is not mistaken for other skin disorders. The clinician must distinguish ulcer psoriasis from conditions like eczema, basal cell carcinoma, or even infections like cellulitis.
Common conditions to rule out include:
- Eczema: Itchiness and inflammation similar to psoriasis but lacks the classic scaling.
- Infectious lesions: Bacterial or fungal infections may mimic the appearance of psoriasis but often present with different symptoms.
- Lichen planus: Another inflammatory condition that may have ulcerative potential yet has distinct features.
The diagnostic process is intricate and may involve further tests, including cultures or allergy tests, to refine the diagnosis. This comprehensive approach to differential diagnosis not only secures the proper labeling of the skin condition but also guides the therapeutic pathway.
Accurate diagnosis is not simply about lab tests. It encompasses patient history, clinical observations, and sometimes, collaborative assessments across specialties.
A thorough diagnosis ensures that treatment strategies can be optimally aligned with the patient’s unique presentation of ulcer psoriasis, promoting better management and outcomes.
Impact on Quality of Life
The prevalence of ulcer psoriasis goes beyond its physical manifestations. This condition significantly influences the quality of life of affected individuals. Understanding its impact is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. It is crucial to address not only the physical aspects but also the psychosocial and economic factors associated with ulcer psoriasis. All these components interplay to shape the experiences of those living with the condition, determining their overall well-being.
Physical Burden
The physical burden of ulcer psoriasis can be substantial. Lesions that develop on the skin can be painful and bothersome. The discomfort can hinder daily activities, such as personal hygiene or physical exertion. Furthermore, as ulcer psoriasis progresses, mobility might be affected due to painful areas on the body.
- Individuals often report feelings of fatigue due to the body's fight against inflammation and irritation.
- The need for ongoing treatments and dermatological care can add to the strain, leading to a feeling of being overwhelmed.
Managing symptoms effectively is essential to alleviate this physical burden. Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop tailored treatment strategies that address their unique needs.
Psychosocial Effects
Ulcer psoriasis often has profound psychosocial consequences. The visible nature of the condition can lead to social stigma and isolation. Patients may experience anxiety or depression because of the perceptions others may have about their skin condition.
- Social interactions can become uncomfortable. Individuals may avoid situations that may expose their skin, contributing to loneliness.
- The psychological impact can affect self-esteem and lead to body image issues.
Support systems play a vital role in mitigating these effects. Encouragement from family, friends, and support groups can provide comfort. Additionally, addressing mental health alongside physical health can contribute to improved quality of life.
Economic Implications
The economic implications of ulcer psoriasis are significant and multifaceted. The costs associated with treatments can be extensive. Patients often face expenses for topical therapies, systemic medications, and regular physician visits.
- Insurance coverage might not fully address the financial burden, leading to out-of-pocket costs.
- Moreover, the condition can result in loss of productivity if individuals miss work due to severe symptoms or flare-ups.
Addressing these economic concerns is vital for patients. Solutions may include exploring financial assistance programs, patient advocacy organizations, or discussing with healthcare providers about more affordable options.
"Understanding the various impacts of ulcer psoriasis is crucial to provide comprehensive care and support for those affected."
Treatment and Management Strategies
Effective management of ulcer psoriasis is crucial due to its chronic and impactful nature. The treatment approach aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and improve the patient's quality of life. As the condition can manifest differently among individuals, it is imperative to tailor management strategies to each patient's specific needs. Options often vary from topical applications to systemic therapies depending on the severity of the disease.
Topical Therapies
Topical therapies serve as a first line of defense in managing ulcer psoriasis. They are applied directly to the affected skin and can help reduce inflammation, scaling, and itching. Common topical agents include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and retinoids.
- Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents and help decrease swelling and redness. They are available in various strengths. Stronger formulations are often used for thicker plaques or areas of severe involvement.
- Vitamin D analogues, such as calcipotriene, normalize skin cell production. They can be used in conjunction with corticosteroids to enhance therapeutic effects, reducing the risk of side effects from corticosteroids alone.
- Topical retinoids, like tazarotene, can help in skin turnover regulation. These agents also support reducing inflammation and are especially useful when combined with other treatments.
Topical therapies are generally well tolerated. However, their effectiveness can decrease as plaques become more widespread or severe.
Systemic Treatments
For cases where ulcer psoriasis is more extensive, systemic treatments may be required. These therapies work throughout the body and can be delivered orally or via injection. The benefits of systemic treatments include their ability to manage severe inflammatory responses and greater improvement in symptoms.
- Methotrexate is a classic systemic agent that suppresses the immune system. It is often favored for its experience and effectiveness.
- Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system. Examples include adalimumab and ustekinumab. They are particularly effective for moderate to severe cases and may significantly improve the quality of life.
- Oral Retinoids, such as acitretin, can also be beneficial in treating ulcer psoriasis. They are used primarily in cases resistant to other therapies, although they come with their own set of side effects and considerations.
Systemic treatment must be monitored closely due to potential side effects, making regular consultations with healthcare providers essential.
Phototherapy Options

Phototherapy involves using specific wavelengths of light to treat ulcer psoriasis. This strategy is beneficial for moderate to severe cases that do not respond sufficiently to topical therapies alone.
- UVB Phototherapy utilizes narrowband ultraviolet B light. This type of therapy can lead to significant improvements for many patients, promoting skin healing. Sessions usually occur two to three times a week.
- PUVA combines the medication psoralen with UVA radiation. This dual approach can be effective, but it is subject to more stringent observation due to potential long-term effects, such as skin aging and increased cancer risk.
- Excimer Laser is another targeted treatment for localized plaques. It delivers high-intensity light to specific areas and can be beneficial when treating isolated lesions.
Phototherapy can provide substantial benefits, but depending on the type, there may be considerations required such as timescales for treatment and potential side effects.
The choice of treatment for ulcer psoriasis should be individualized and regularly reviewed with healthcare providers to ensure optimal management of this chronic condition.
Recent Advances in Research
Research on ulcer psoriasis is continually evolving, shedding light on various aspects of this complex condition. Understanding these advances is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. In recent years, several key areas have become focal points in the research landscape, offering significant insights into the disease's underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches.
Clinical Trials and Studies
Clinical trials are fundamental in evaluating the effectiveness of new treatments for ulcer psoriasis. These trials often focus on both systemic and topical therapies, investigating their safety and efficacy in diverse populations. Recent studies have provided promising results for several biologics and small molecules. For instance, trials featuring agents like Secukinumab and Ixekizumab have shown positive outcomes in reducing lesion severity and improving patients' quality of life. Each trial contributes valuable data that helps refine treatment protocols, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care based on the latest evidence. Researchers emphasize the importance of long-term follow-up to assess the sustainability of treatment benefits.
Emerging Therapeutic Agents
The exploration of emerging therapeutic agents has been a game-changer in ulcer psoriasis management. Researchers are investigating novel compounds and biologics that target specific pathways involved in the disease process. For example, Brodalumab focuses on interleukin-17 pathways, demonstrating enhanced efficacy in moderate to severe cases of psoriasis.
Moreover, emerging small molecules, like Aprepitant, are being examined for their anti-inflammatory properties. These agents present significant potential not only for treating existing lesions but also for tackling underlying pathophysiological processes. As studies on these agents advance, they may become key components in integrative treatment plans, emphasizing precision medicine tailored to individual patients' needs.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, the future of research in ulcer psoriasis is promising. Several avenues are under exploration that could transform the understanding and treatment of this condition.
- Personalized Medicine: More studies are looking into the genetic and epigenetic profile of patients to tailor therapies specifically to their unique biological makeup.
- Microbiome Studies: Recent research has highlighted the role of skin microbiota in psoriasis pathology, opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions that focus on restoring microbial balance.
- Longitudinal Studies: Continuous observational studies will provide insight into long-term treatment outcomes, side effects, and potential comorbidities associated with different treatment regimens.
This multidisciplinary approach not only seeks to improve immediate clinical outcomes but also aims to enhance our understanding of the holistic effects of ulcer psoriasis on patients' lives.
Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support play crucial roles in the management of ulcer psoriasis. Affected individuals often face various challenges related to the condition, which can significantly impact their daily lives. Understanding the disease, engaging in effective self-management strategies, accessing available resources, and connecting with support networks can empower patients and aid in improving their quality of life.
Strategies for Self-Management
Self-management is a key component in dealing with ulcer psoriasis. Patients can benefit from developing personalized strategies that fit their lifestyles. This includes:
- Daily Skin Care Routines: Establishing a consistent skin care regimen can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Gentle cleansers and appropriate moisturizers can support skin integrity.
- Diet and Nutrition: Some patients find relief by adhering to specific diets that eliminate potential triggers. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins while avoiding inflammatory foods may improve skin condition.
- Stress Management: Stress often exacerbates skin conditions. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga and other relaxation methods can assist patients in minimizing stress and improving their overall wellbeing.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping a symptom diary helps in identifying triggers and patterns related to flare-ups, enabling better management decisions.
Resources for Patients
Access to reliable resources is essential for those dealing with ulcer psoriasis. Notable resources include:
- Educational Websites: Websites like Wikipedia and Britannica provide comprehensive information about the condition, treatment options, and ongoing research.
- Medical Journals: Accessing peer-reviewed articles can keep patients updated on the latest studies and treatment protocols.
- Apps for Tracking Symptoms: Mobile applications can help patients monitor symptoms and treatment effects over time. These may enhance communication with healthcare providers during visits.
"Education empowers patients, leading to better health outcomes."
Support Groups and Networks
Support groups can be invaluable for individuals living with ulcer psoriasis. Connecting with others who share similar experiences fosters a sense of community and support that can be crucial for mental health and emotional wellbeing. Key considerations include:
- Local and Online Groups: Many organizations offer local support groups, while online communities such as Reddit provide platforms for discussion and support, regardless of geographical limitations.
- Patient Advocacy Organizations: Joining organizations dedicated to skin health can provide access to resources, advocacy, and information about additional support services. These can assist in raising awareness and improving the quality of treatment for those with the condition.
- Engagement in Shared Experiences: Participating in support circles or forums can help individuals realize they are not alone in their struggles, promoting shared knowledge and coping strategies.
The End
In the realm of ulcer psoriasis, understanding the complexities of the condition is crucial. This article has provided a thorough examination of the disease's pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies. Each section contributes to a broader understanding of how ulcer psoriasis affects individuals' lives and the available avenues for treatment.
Summary of Key Points
- Pathophysiology: Ulcer psoriasis is driven by immune system dysregulation and genetic predispositions, leading to skin barrier impairment.
- Clinical Manifestations: Symptoms often include persistent lesions, significant discomfort, and co-morbid conditions that further complicate patient care.
- Diagnosis: Effective diagnosis requires a combination of clinical assessments and histopathological evaluations to differentiate it from other similar conditions.
- Quality of Life: Ulcer psoriasis can severely impact physical and emotional well-being, affecting daily activities and social interactions.
- Treatment: Current management strategies encompass topical therapies, systemic treatments, and emerging phototherapy options. Ongoing research aims to discover new therapeutic agents.
References for Further Reading
For those seeking to delve deeper into ulcer psoriasis and related topics, the following resources can be invaluable:
- Wikipedia on Psoriasis
- Britannica on Psoriasis
- Reddit Community Discussions
- Facebook Groups for Support
By articulating the details surrounding ulcer psoriasis, we can foster a collective awareness that might lead to better patient outcomes and contribute to ongoing advancements in treatment options.















